Put in a bag of rice. That’s the most common answer. You can also bury your phone in the soil.
But why rice can be used to suck out moisture from inside of your mobile phone. Some said rice is dry (so are other materials such as paper), and some said it has a high affinity for drawing out moisture. But how does rice do that?
The answer is simple soil physics that said water moves from a high potential to a low potential. All materials that absorb water can be related to their water potential, which is the energy of which water is held by the particles (via capillary and adsorption forces). It is also the potential for water to move, or do work, and sometimes called suction, or water tension. This energy can be expressed in terms of Joules per kg (of material) or units of pressure (Pascal). Water potential in the environment is almost always less than zero.
In soil science, the relationship on how much water a soil can hold as a function of its potential (or energy) is called a moisture characteristic curve. Naturally, all hydrophilic materials have their own moisture characteristic curve.
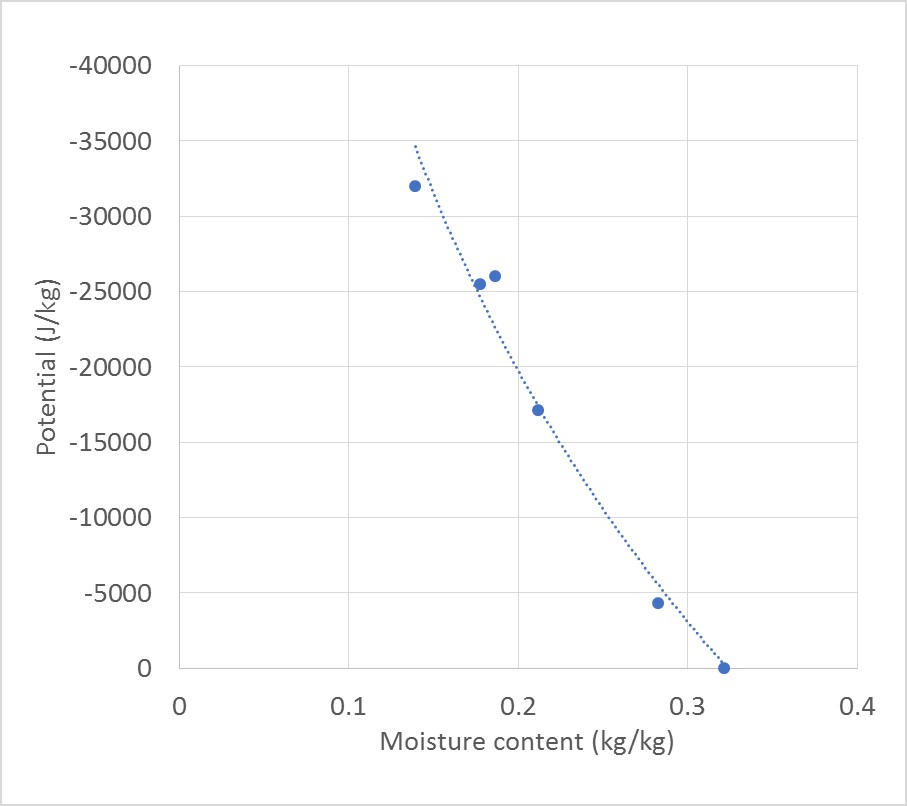
We measured the moisture characteristic of rice grains (Sunrise medium grain) using the “filter paper method”. The graph below shows the amount of water the rice can hold as a function of the energy holding it. Rice, as in the bag, when we bought it contains about 18% moisture. But what is interesting that its potential is quite low (around -32,000 J/kg or kPa). That means if a phone with moisture in it has a lower potential (free water has a potential of zero). Having this large potential difference, allows water to move from a wetter condition (higher potential) to dryer condition (lower potential).
There is also a relationship between potential and relative humidity (expressed by Kelvin or Nernst equation). The potential of a dry grain of -32,000 J/kg is equivalent to a relative humidity of about 80% (Humidity in Sydney during autumn). It is considered relatively dry that allows the rice to absorb moisture (which has lower potential). Or in terms of pressure, it 32,000 kPa (or 100 times the pressure of a tyre).
This article is written bu Budiman & Alex.
The water retention curve of a medium-grain rice.


Leave a Reply